
Gas Liquid Chromatography PDF Gas Chromatography Chromatography
Gas chromatography is different from liquid chromatography because the mobile phase is essentially inert, and thus, is only used to carry the vapors; the vapors do not interact with the carrier gas. In LC, the liquid phase also interacts with molecules. Gas chromatography is advantageous because very small sample sizes can be used with minimal

GAS LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY Principles Partition of molecules between
Abstract. Gas chromatography (GC) is a common kind of chromatography used as a piece of analytical science for segregating and investigating exacerbates that can be vaporized without.
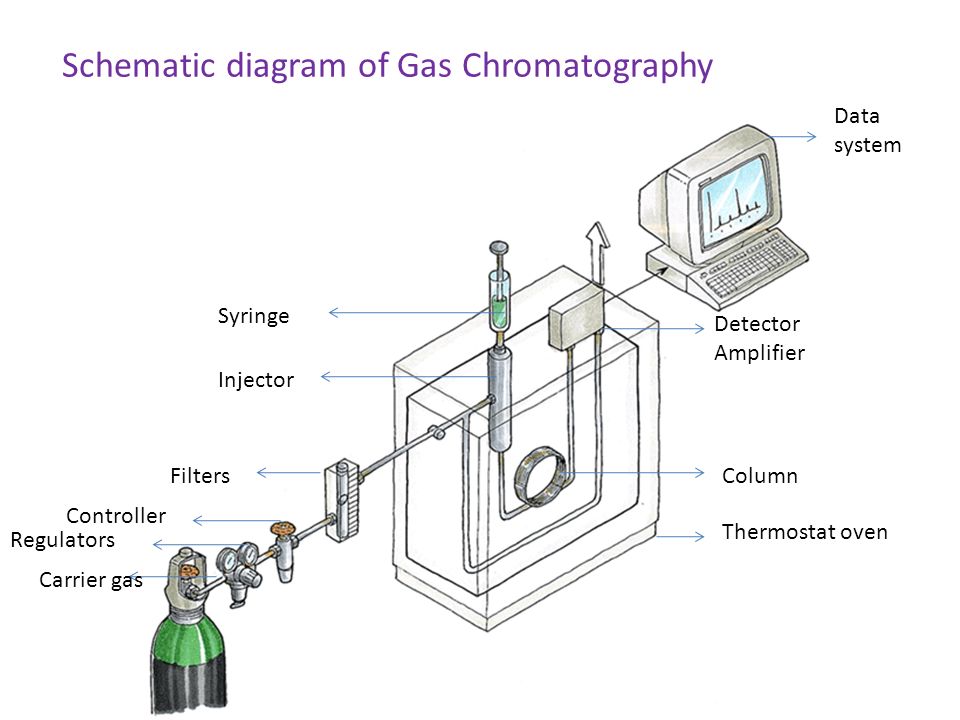
[28+] Schematic Diagram Of Gasliquid Chromatography im7 blog
What Gas Chromatography Is 1 Fundamentals of GC 11 The System A gas chromatographic system consists of: • A regulated and purified carrier gas source, which moves the sample through the GC • An inlet, which also acts as a vaporizer for liquid samples • A column, in which the time separation occurs • A detector, which responds to the components as they occur
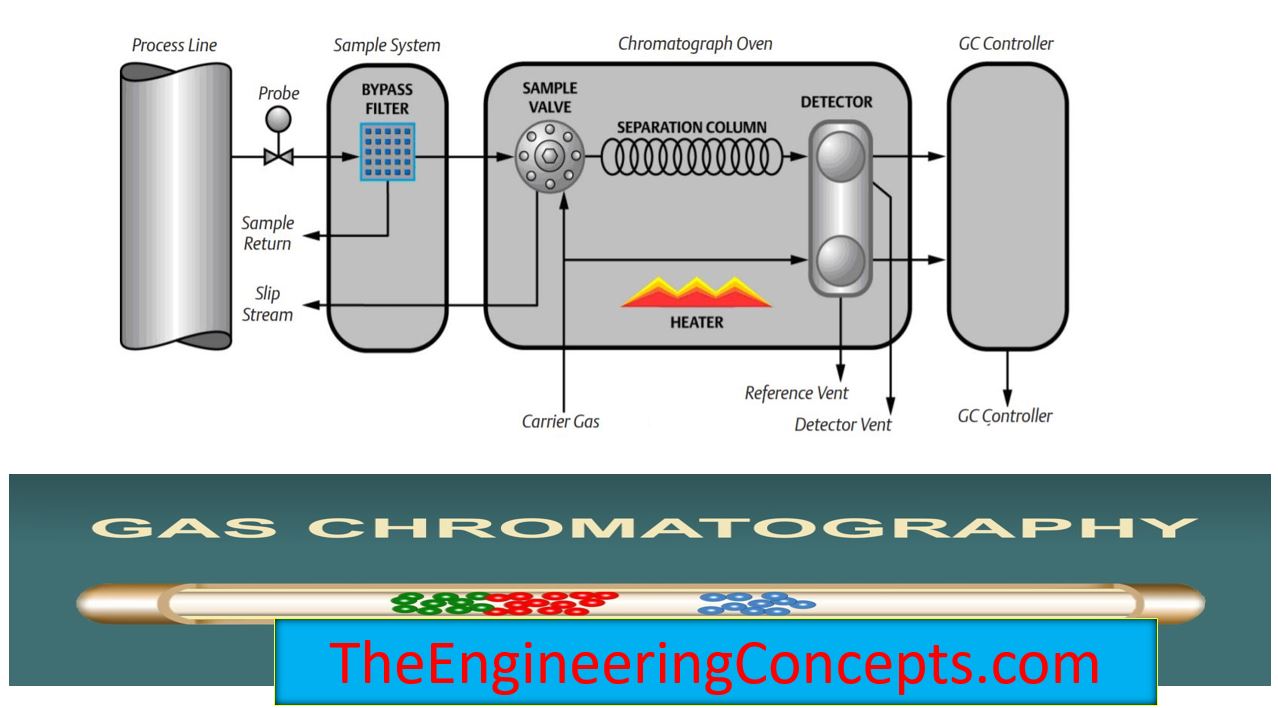
Gas Chromatography Diagram
Gas - liquid chromatography is a form of partition chromatography in which the stationary phase is a film coated on a solid support and the mobile phase is an inert gas like Nitrogen (N2) called as carrier gas flowing over the surface of a liquid film in a controlled fashion. The sample under analysis is vaporized
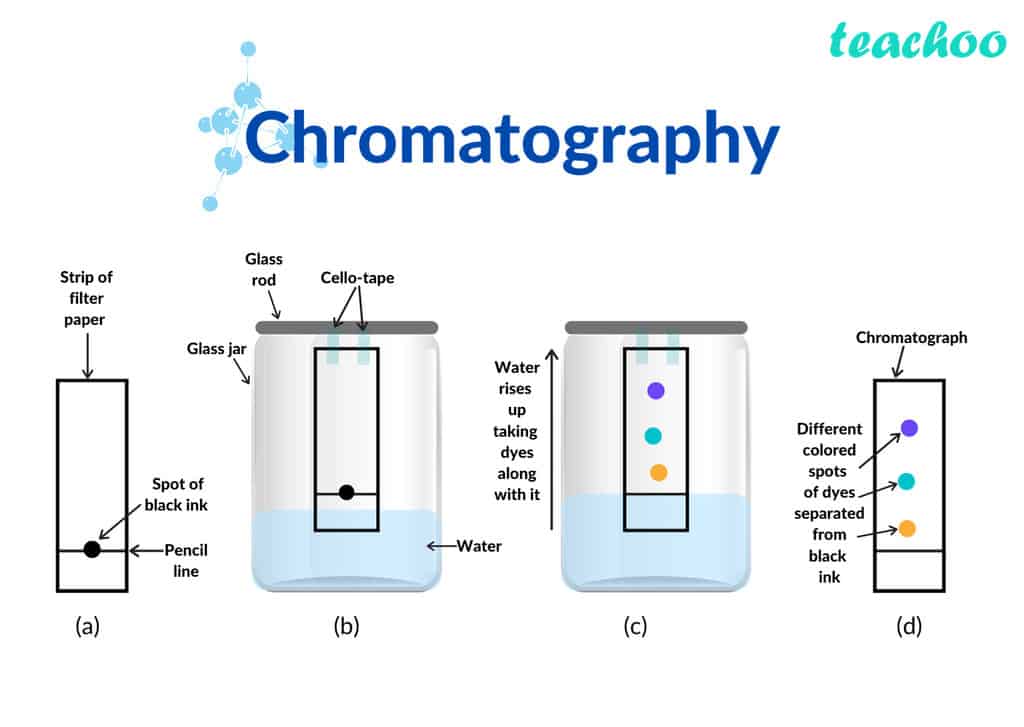
What is Chromatography? Gas Liquid Chromatography, HPLC Chemical Separation Techniques
Gas Liquid chromatography Liquid stationary phase Gas mobile phase Liquid stationary phase is; - Coated on an inert solid support which can be wettable with the liquid stationary phase (Eg: Packed columns) - Made into a fused silica capillary column - Sample should be volatile to move with the gas mobile phase.

GasLiquid Chromatography? Easy Way To Learn Chromatography
A gas chromatograph (GC) is an analytical instrument that measures the content of various volatile components in a sample. The analysis performed by a gas chromatograph is called gas chromatography. Principle of gas chromatography: The sample solution injected into the instrument enters a gas stream which transports the sample into a separation.
.PNG)
Chromatography Presentation Chemistry
Carrying out gas-liquid chromatography. All forms of chromatography involve a stationary phase and a mobile phase. In all the other forms of chromatography you will meet at this level, the mobile phase is a liquid. In gas-liquid chromatography, the mobile phase is a gas such as helium and the stationary phase is a high boiling point liquid.
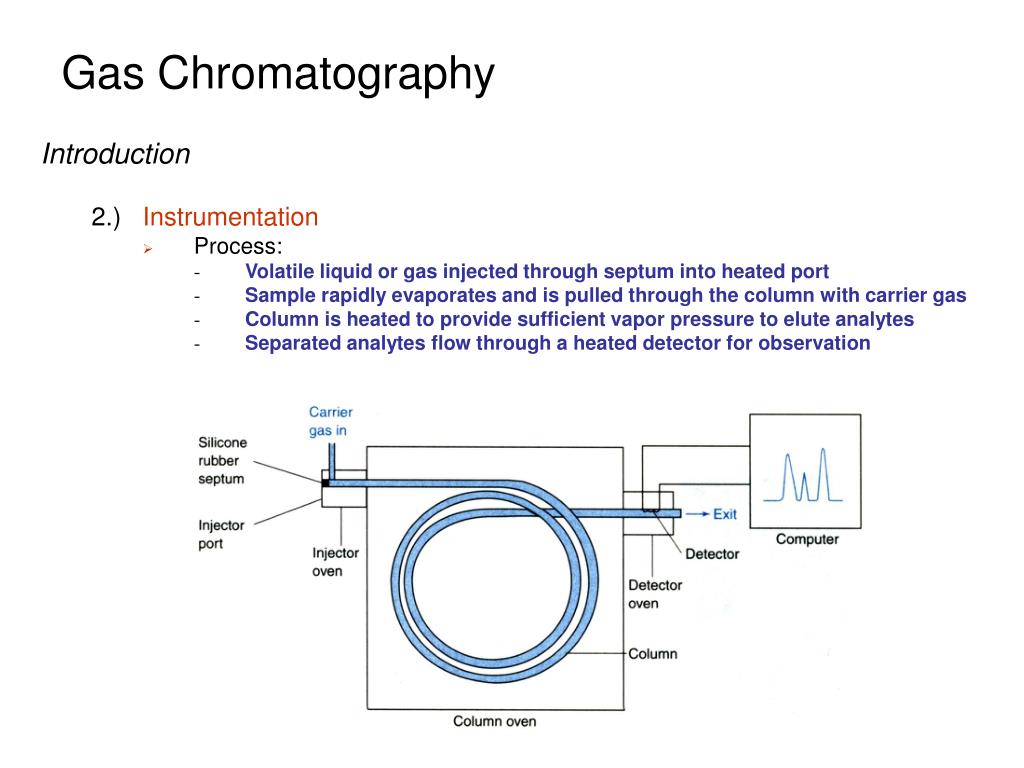
PPT Gas Chromatography PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3200968
Chromatogram (Figure 3.1. 5 a) shows a standard solution of methanol with 2-propanol as the internal standard. From the figure it can be seen that methanol has a higher affinity for the mobile phase (lower K c) than 2-propanol (iso-propanol), and therefore elutes first. Chromatograms (Figure 3.1. 5 b and c) show two samples of biodiesel, one.

Gas Liquid Chromatography YouTube
GC Structure and Fundamentals. Gas chromatograph is an analytical instrument used to analyze the different components in a sample. An analytical method using a gas chromatograph is called gas chromatography (GC). Table 1: Terminologies and Defnitions of Gas Chromatography. Term. Defnition. Chromatography.
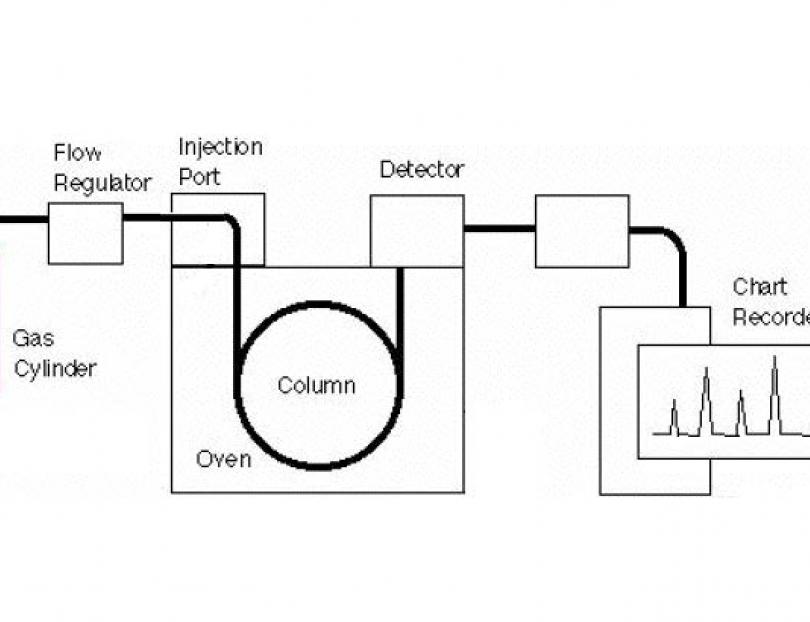
Gas Chromatography Instrumentation Diagram
Mass Spectrometry is an analytical technique that forms ions from atoms or molecules and measures their mass-to-range (m/z) ratios in gas phase. Mass Spectrometry can provide information about molecular and elemental composition and also quantify the abundance of individual chemical components. It is highly selective techniques, meaning that it.

(PDF) Gas Liquid Chromatography
Gas chromatography provides a means for the separation of volatile components of either a gaseous, liquid, or solid mixture based on a partitioning of the mixture's vapor components between two phases. One phase (the stationary phase) is a stationary bed of small particles through which the vapor component travels.
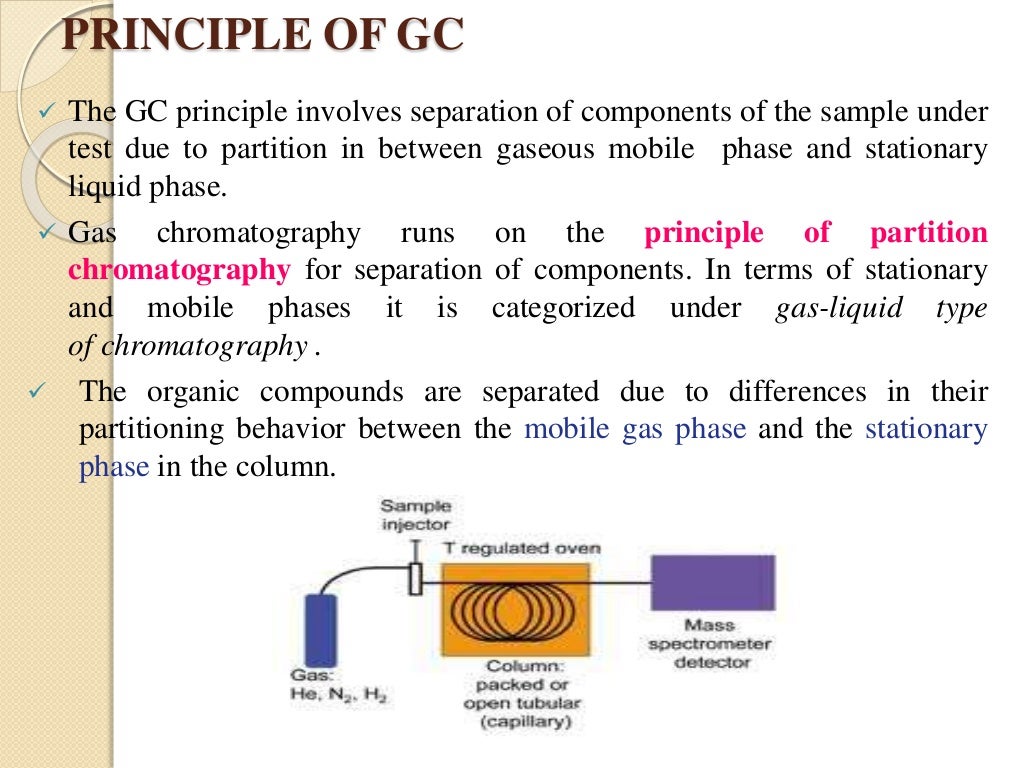
Gas chromatography
Page ID. Gas chromatography is a term used to describe the group of analytical separation techniques used to analyze volatile substances in the gas phase. In gas chromatography, the components of a sample are dissolved in a solvent and vaporized in order to separate the analytes by distributing the sample between two phases: a stationary phase.

Liquid Chromatography vs Gas Chromatography LC Services
See Full PDFDownload PDF. GAS LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY MAGENDIRA MANI ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ISLAMAIAH COLLEGE VANIYAMBADI [email protected] f GAS LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY Gas liquid chromatography (GLC), is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition.

PPT D4 Depressants PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2108440
Gas chromatography is widely used for the analysis of a diverse array of samples in environmental, clinical, pharmaceutical, biochemical, forensic, food science and petrochemical laboratories. Table 27.4.1 provides some representative examples of applications. Table 27.4.1 . Representative Applications of Gas Chromatography. area. applications.

(PDF) Application of Gas chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC MS) in Food Science and Biotechnology
A. GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY • Gas-Liquid chromatography, (GLC) • Mobile phase -Gas (Helium) Carrier Gas Pressure = 4 kg/cm2 • Stationary phase - Column, which is typically "packed" or "capillary". • The stationary phase is adhered to the inside of a small-diameter glass tube (a capillary column) or a solid matrix inside a larger metal tube (a

[Get 31+] Gas Chromatographymass Spectrometry Schematic Diagram
Liquid chromatography can further be 13 divided into ion exchange, separations based on size, and even extended to gel-14 based electrophoretic techniques. This book will provide a basic introduction to 15 different types of liquid and gas chromatography. The relationship between each 16 type of chromatography is illustrated in Figure 1.1. 17